Purpose:
The purpose of this experiment was to measure planks constant using the spectral lines of different colored LED’s. The LED’s wave length was measured using the same system as used in the previous experiment. The Voltage through the LED was measured and graphed with the frequency and the slope of that line was expected to be Plank’s constant.
Method:
Two rulers were set up in an L shape and at the end of one of the rulers was an LED with the gradient at the front of the ruler. To the right of the LED was another ruler that was used to measure how far the spectral lines appeared to be from the source when looking through the gradient. A measured Voltage was sent through the LED and the Spectral line were measured to determine the wavelength of the LED. This was used in determining the frequency.
| D (cm) | L (cm) | Wavelength (nm) | Voltage (V) | |
| Red | 191.85 | 36.3 | 641.9 | 1.81 |
| Orange | 191.85 | 33.9 | 592.4 | 1.88 |
| Green | 191.85 | 31.8 | 529 | 2.48 |
| Blue | 191.85 | 28.4 | 475.6 | 2.58 |
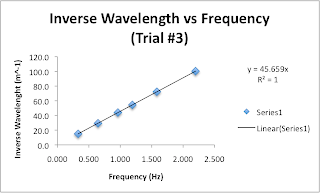
The Energy was determined by multiplying the voltage with the charge of a electron.
| E (J) | 1/wavelength | |
| Red | 2.90E-19 | 1.56E+06 |
| Orange | 3.01E-19 | 1.67E+06 |
| Green | 3.97E-19 | 1.89E+06 |
| Blue | 4.13E-19 | 2.10E+06 |
h=qV/f
Using the relationship above plank's constant which is known to be 6.626E-34 was recorded as:
Red 6.21E-34
Orange 5.94E-34
Green 7.00E-34
Blue 6.55E-34
Conclusion:
The average experimental value of h came out to be 6.43E-34. This value when compared to the excepted plank's constant has an error percentage of 3.03% which is an acceptible verification of plank's constant.
Using the relationship above plank's constant which is known to be 6.626E-34 was recorded as:
Red 6.21E-34
Orange 5.94E-34
Green 7.00E-34
Blue 6.55E-34
Conclusion:
The average experimental value of h came out to be 6.43E-34. This value when compared to the excepted plank's constant has an error percentage of 3.03% which is an acceptible verification of plank's constant.